CLIMATE OF LIBYA.

CLIMATE ZONES OF LIBYA
Under the Koppen-Geiger classification system, there are five climatic zones in Libya: (i) Hot Arid Desert Climate; (ii) Cold Arid Desert Climate; (iii) Hot Arid Steppe Climate; (iv) Cold Arid Steppe Climate; and (v) Temperate Hot Dry Summer Climate.
As the majority of Libya is home to the Sahara desert, the main climate of the country is classified as being of the Hot Arid Desert Climate. However, the majority of the population of Libya reside in and around the urban areas of Tripoli, Benghazi and Misrata, which are cities along the Mediterranean coast. These coastal regions are classed as being of the Hot Arid Steppe Climate. The Eastern coastal areas of Derna and Al Marj are recognised as being of the Temperate Hot Dry Summer Climate.
THE ARID HOT DESERT CLIMATE
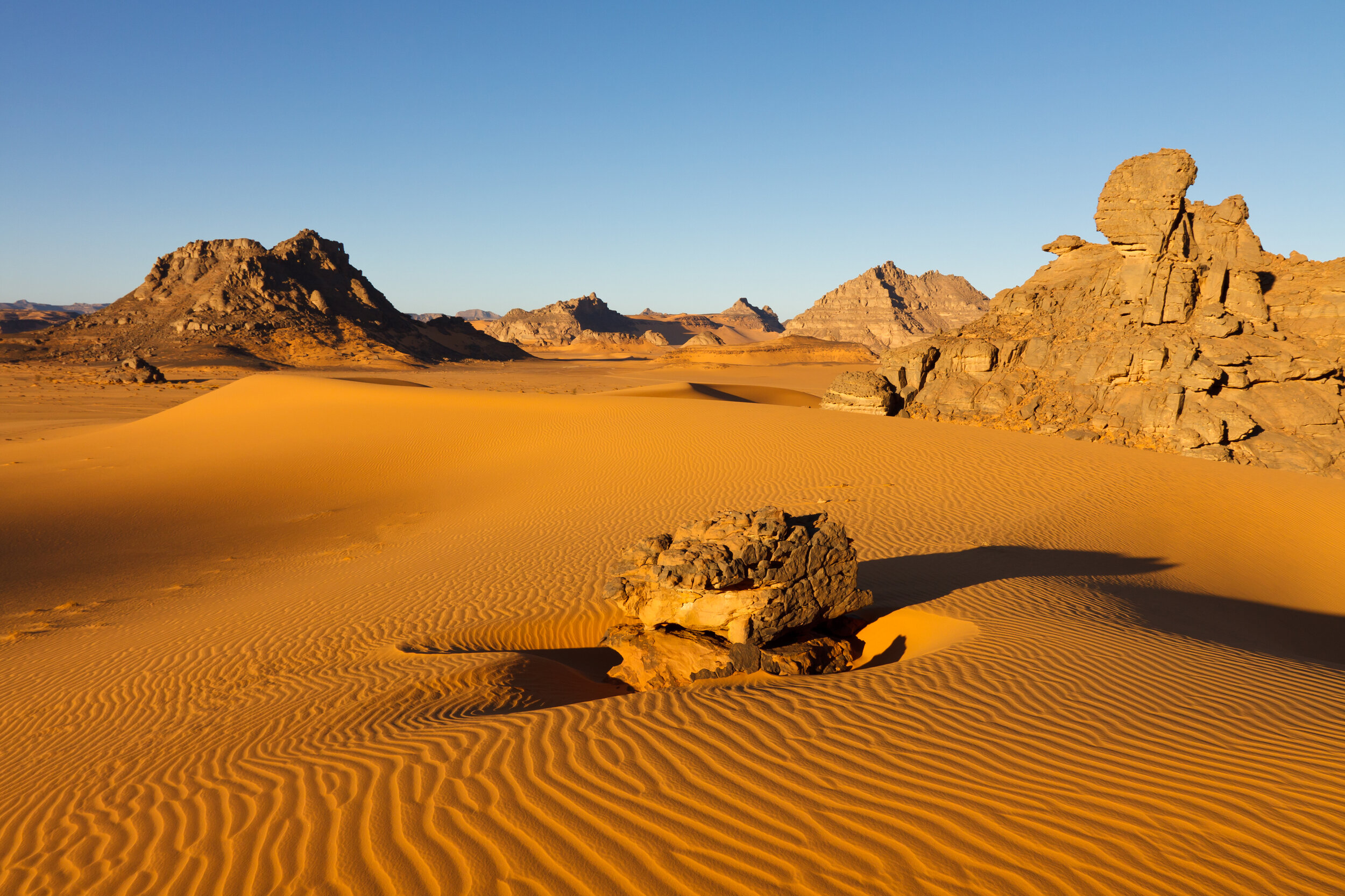
The Saharan Desert covers the majority of this climate zone in Libya and is considered by some to be one of the least hospitable places on Earth. The area is hot, arid and can experience extreme variations of temperature within a day, with summer daytime temperatures reaching over 50C and dropping drastically during the evening1. Winter sees daytime temperatures in the region of 27C, falling to well below freezing overnight, with the lowest ever recorded temperature of -15C being in the Tibesti Mountains, which though mainly situated in Chad, has a small extension in southern Libya2.
Precipitation is rare and irregular in this climate, with an average annual rainfall of just 0-50mm per year and an annual average humidity of below 35%. Al-Kufrah, an oasis town in southeastern Cyrenaica, has the title of one of the driest areas of the world, receiving only 0.0338 inches of rainfall in any given year4.
The Sahara Desert in Libya

AL KUFRAH
THE GHIBLI
Ghibli, is a dry, hot, desert dust bearing wind, that spreads south to south easterly across Libya, descending from the interior highlands and sweeping across the Libyan Desert towards the Mediterranean Sea. The Ghibli occurs mainly during the spring and early summer, but can also occur throughout the year. It usually lasts between one to four days and carries large quantities of sand dust which turn the Libyan sky red and greatly reduce visibility5.
Sandstorm in the Sahara Desert
THE ARID HOT STEPPE CLIMATE
The areas of Libya included in this climatic zone are part of a small band of semi-arid steppe, which include the regions of the Al Jufrah Plain, the Nafusah Plateau, Tripoli to the North West of Libya and a small area of the Derna district to the North East. This climate classification covers a region that receives rainfall below potential evapotranspiration (the sum of water evaporation and transpiration from surface to atmosphere), but not as low as the Arid Desert Hot climate. Also, comprising of two different regions, means the conditions in this climate zone vary from the North West to the North East6.
Old Town of Yefren, Nafusa Plateau
North West nad North East Libyan Arid Hot Steppe Climate
The temperature in the North West region sees an average August temperature of 26.5C, but has on occasion been known to reach 44C. Nightfall in August sees a lowering to 18C. January registers the lowest temperature at an average of 10.2C, falling to an average of 3C overnight. The temperatures in the North East during August can reach 29C during the day and stay at a very warm 24C through the night.The winter months see an average of 21C in daylight hours and a fall to an average of 10C at night7.
Region of the Al Jufra Plateau
Precipitation in the North West is at its lowest in July and August when it registers 0mm of precipitation, rising to its highest level of 57mm in January. However, the North East experiences a low of 1mm of precipitation in June, rising to 260mm in November8.
Humidity in both areas is considered high, with the average in the North West being 68% and the North East with a slightly higher average of 73%9.
The wind speed varies in both regions. The North West shows average speeds of between 15 and 23km per hour throughout the year. Whereas the North East details average speeds of between 11.6 and 21.96km per hour, the lowest being registered in October and the highest in February10.

haruj VOLCANIC field, AL JUFRA
THE COLD DESERT CLIMATE
The Cold Arid Desert Climate of Libya is found in relatively small areas of the country, these include the southern areas of the northern regions of Benghazi and Derna. Also included in this climate is Bikku Bitti, which is the highest mountain in Libya at 2,266m. It is located on the Dohone spur of the Tibesti mountain range, situated on the border of southern Libya11. Bikku Bitti is one of the least accessible parts of the Sahara Desert12.
These areas are recognised as having hot, dry weather during the summer months, although temperatures do not usually reach the highs of the Hot Desert Climate. August, being the hottest month, often sees temperatures reaching an average of 24C. The winters in this climate tend to be dry and cold, with January seeing daytime temperatures drop to an average of between 8 and 10C.
The altitude of these regions lead to a higher than average Libyan precipitation throughout the winter months, with Al Himadah in Benghazi seeing an average of 335mm per year, with the majority of rainfall occurring in the months from October to February, whilst Martuba in Derna has a far lower average precipitation of 168mm. However, the southern location and extreme altitude of Bikku Bitti means that the area is sometimes devoid of rainfall for years at a time, and is classified as unfit for human habitation.

TIBESTI MOUNTAINS, SOUTHERN LIBYA
THE COLD STEPPE ARID CLIMATE
The Cold Arid Steppe Climate includes areas of Al Kharruba, Al Jabal Akhdar and Derna. This climate tends to be located in the higher altitude areas of the temperate zones, particularly those adjoining the Mediterranean climate zones13.
The temperatures in this climate usually favour warm to hot arid summers, and cooler winters, with summer daytime temperatures reaching an average high of 34C and a night time low of 20C. The winter months are colder with an average daytime high of 15C and a night time low of 7C14.
The precipitation of the zone varies throughout the year, with an average annual rainfall of 260mm, the majority of which occurs between the months of October and February. Humidity levels for the zone are fairly consistent, ranging from 57% in May to 68% throughout July15.
Region of Derna
via Wikimedia Commons
THE TEMPERATE DRY HOT SUMMER CLIMATE
This climatic zone can be found in the eastern parts of the northern coast of Libya, and includes the very northernmost areas of Al Marj, Al Jabal Al Akhdar, and Derna16. The temperatures vary throughout the year, with the region seeing an average daytime summer temperature of 23-24C, during the months of July and August, and falling to a low of 12.5C in January and February17.
Precipitation is seen mainly in the month of November, with an average rainfall of 254mm18. Humidity in the eastern region is high, and ranges between 69% to 78%, throughout the year, with July showing the highest annual level19.
Wind speeds in these regions average 23km per hour, with a high of 34.8km in July, which sees the highest level, with gusts reaching upto 37.9km.Footnote20.
Ras Al Helal Port - Jabal Akhdar
Maher27777, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons.
FOOTNOTES.
Geography of Libya.” Fanack.com, August 31, 2020. https://fanack.com/libya/geography/.
“Climate.” Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, inc. Accessed January 12, 2021. https://www.britannica.com/place/Sahara-desert-Africa/Climate.
Reports, Staff. “Many Homes Are Drier Than the Sahara Desert.” Oklahoman.com. Oklahoman, December 12, 1993. https://oklahoman.com/article/2450798/many-homes-are-drier-than-the-sahara-desert.
Markings, Samuel. “Where Is the Location of the Savanna?” Sciencing, March 2, 2019. https://sciencing.com/location-savanna-7386021.html.
Geography of Libya.” Fanack.com, August 31, 2020. https://fanack.com/libya/geography/.
“Climate Details in Libya.” Worlddata.info. Accessed January 21, 2021. https://www.worlddata.info/africa/libya/climate.php.
David Robinson BA(Hons), PGCE. The Climate Of Libya. Accessed January 21, 2021. http://www.geography-site.co.uk/pages/countries/climate/libya_climate.html.
“Climate and Average Weather in Libya.” World Weather & Climate Information. Accessed January 21, 2021. https://weather-and-climate.com/average-monthly-Rainfall-Temperature-Sunshine-in-Libya.
“Climate.” Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, inc. Accessed January 21, 2021. https://www.britannica.com/place/Libya/Climate.
“What Is the Weather, Climate and Geography like in Libya.” World Travel Guide, May 26, 2019. https://www.worldtravelguide.net/guides/africa/libya/weather-climate-geography/.
“Geography of Libya.” Fanack.com, August 31, 2020. https://fanack.com/libya/geography/.
“Ginge Fullen.” SummitPost.org. Accessed January 16, 2021. https://www.summitpost.org/ginge-fullen/333351#chapter_1.
“Climate Details in Libya.” Worlddata.info. Accessed January 21, 2021. https://www.worlddata.info/africa/libya/climate.php.
David Robinson BA(Hons), PGCE. The Climate Of Libya. Accessed January 21, 2021. http://www.geography-site.co.uk/pages/countries/climate/libya_climate.html.
“Climate and Average Weather in Libya.” World Weather & Climate Information. Accessed January 21, 2021. https://weather-and-climate.com/average-monthly-Rainfall-Temperature-Sunshine-in-Libya.
“Climate Details in Libya.” Worlddata.info. Accessed January 21, 2021. https://www.worlddata.info/africa/libya/climate.php.
David Robinson BA(Hons), PGCE. The Climate Of Libya. Accessed January 21, 2021. http://www.geography-site.co.uk/pages/countries/climate/libya_climate.html.
“Climate and Average Weather in Libya.” World Weather & Climate Information. Accessed January 21, 2021. https://weather-and-climate.com/average-monthly-Rainfall-Temperature-Sunshine-in-Libya
“Climate.” Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, inc. Accessed January 21, 2021. https://www.britannica.com/place/Libya/Climate.
“What Is the Weather, Climate and Geography like in Libya.” World Travel Guide, May 26, 2019. https://www.worldtravelguide.net/guides/africa/libya/weather-climate-geography/.